Aluminum Casting: Methods, Common Alloys & Applications
Aluminum casting is a process that molds metal into parts. This article will explore its methods, applications, and commonly used casting alloys.
Aluminum's unique properties make it ideal for casting. It has a relatively low melting point and high fluidity when molten, allowing precision when cast. Once solidified, it forms lightweight yet durable components, which can be used to create countless products in our daily lives, from kitchenware, lighting, automotive, to electronics, and more.
In this article, we will delve into various types of aluminum casting processes, casting alloys, and their common applications, to help you understand this versatile manufacturing technique.
What is Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting is a manufacturing process that involves heating aluminum and pouring the molten metal into a mold designed for the desired product. Upon cooling and solidification, the aluminum assumes the shape of the mold cavity. Then, the finished metal part can be extracted and applied to subsequent processes such as machining or assembly.
The history of aluminum casting dates back to 1854, with English chemist Henry Bessemer as the earliest known pioneer to lay the groundwork by creating a pressure-casting-like process. Unfortunately, the resources for this method were hard to come by at the time, but with advancements throughout the years, there have been breakthroughs in the extraction and refining processes. Namely, the Hall-Héroult process has significantly reduced production costs and made aluminum more accessible.
As of today, aluminum casting has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, with its global market valued at USD 90.97 billion in 2022. Moreover, this figure is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030, reflecting the growing importance of aluminum casting in various industries.
How to Cast Aluminium: 6 Aluminum Casting Processes
While the basic principle remains consistent, there are different methods to cast aluminum with varying mold creation and filling techniques, resulting in distinct product precision and cycle times. Hence, to achieve optimal results for your specific project, you should consider factors such as part complexity, production volume, and budget constraints when selecting an aluminum casting process.
This section will explore the 6 common casting methods for aluminum, including:
We will also touch on some other methods that derive from the main processes, but won’t go into too much detail for now.
Die Casting
Die casting is a process that uses high pressure to pour molten aluminum into a precisely engineered steel mold. This method excels at producing parts with excellent strength, dimensional accuracy, and consistent quality, even if the product design has thin walls. The surface of these products also boasts a great finish, so it often requires minimal treatment or machining.
While the higher upfront costs for die-casting molds are less cost-effective for low-volume productions, the molds are quite durable and capable of being used up to 80,000 times before requiring replacement. Die casting also has a rapid production speed, making it ideal for mass production.
Die casting techniques can also be further categorized as hot chamber, cold chamber, and injected metal assembly (IMA). There is also a method called vacuum die casting that removes most gases within the mold cavity before injecting the molten metal, creating a near-vacuum condition that minimizes air pockets and enhances the overall quality of the cast. If you want to learn more, you may refer to our article on the different types of die casting processes.
Investment Casting
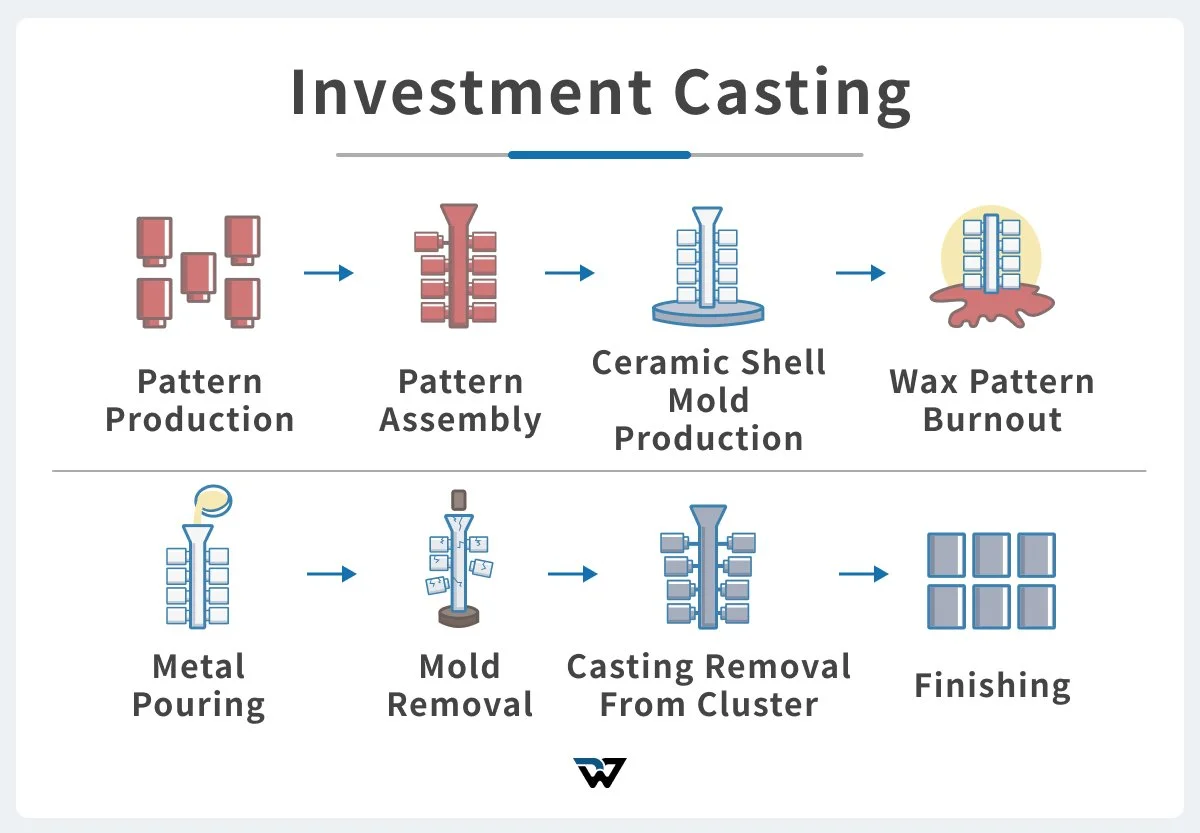
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting or ceramic mold casting, is a process that yields components with high accuracy and intricate detail. It begins with creating a wax pattern of the desired part. These wax patterns are then assembled into a tree-like structure and coated with a ceramic slurry to create a protective shell.
Once the ceramic shell has hardened, the wax will be melted and removed, leaving behind a cavity with the shape of the original wax pattern. Molten aluminum will be poured into this cavity for casting. After cooling, the ceramic shell will be broken away to reveal the final product.
Investment casting is particularly useful for producing highly complex components, which may be difficult to achieve with other methods. Yet, due to the complex tooling and production process, the cost of this method is generally higher.
One notable variation of the investment casting method is lost foam casting, which uses expandable polystyrene foam as the pattern material instead of wax. Though lost foam casting costs less, it has limitations for handling intricate product designs.
Gravity Casting
Gravity casting relies solely on the force of gravity to draw the molten aluminum into the mold cavity. It is also called permanent mold casting, as the molds for this process are typically made from high-temperature resistant metals, enabling repeated use.
Compared to other casting methods, this gravity casting is relatively straightforward and requires less complex equipment, reducing labor and production costs. Plus, due to its simplicity, the equipment can usually accommodate bigger mold cavities to create larger castings.
Nevertheless, gravity casting offers slightly less design complexity and accuracy when compared to die casting or investment casting. Additionally, the slower cooling rate associated with gravity casting can extend production cycle times, making it more suitable for lower to medium-volume production runs.
Sand Casting
In sand casting, the mold is made by mixing sand particles and an inorganic binding agent, such as water with clay to ensure stability. A cavity shaped like the desired product will be formed within the sand using wood or metal, before aluminum is poured in to be cast. The sand will then be completely removed to extract the finished product.
This method offers significant flexibility in terms of part design and size. Furthermore, the initial tooling costs for sand casting are relatively low compared to other processes, as the molds are disposable, making them suitable for small-scale production of individual one-shot parts. Yet, it's essential to note that sand castings provide lower dimensional precision and less appealing surface finish.
An alternative to sand casting is shell mold casting. Instead of creating a full sand mold, it uses a resin-bonded sand mixture to form a thin, hardened shell around the design pattern before pouring the molten aluminum into the cavity. With this, shell mold casting improves the precision of the product design while maintaining the rapid mold creation of traditional sand casting.
Open Mold Casting
Open mold casting is one of the most basic methods where molten aluminum is poured into a simple, open cavity. The mold can be made out of brick, stone, steel, or sand-based materials, and unlike other casting processes that utilize enclosed molds, the molten aluminum will be directly exposed to open air as it cools and solidifies.
This method is typically used for producing large, irregularly shaped castings or ingots. Although open mold casting generally offers lower production costs due to its simplicity, its results are much less intricate and thus require further processing, such as forging or machining to achieve design accuracy and a smoother finish.
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting or roto casting is a manufacturing process that leverages centrifugal force to create hollow cylindrical components. By rotating a mold at high speed while pouring in molten aluminum, the centrifugal force distributes the material evenly against the mold's inner wall, resulting in a dense and uniform casting.
This method is particularly effective for producing pipes, tubes, and other cylindrical shapes. Moreover, the centrifugal force exerted during the casting process compacts the molten metal, enhancing the material's overall integrity and achieving a consistent wall thickness, thus reducing the need for machining. Even so, the downside to this process is the limited shapes that can be formed within a rotating mold.
Aluminum Casting Process Comparison
| Process | Precision | Surface Finish | Production Time | Cost | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High | Excellent | Short | Product: Low Mold: High |
Mass production of intricate components |
| Investment Casting | Excellent | Excellent | Long | Product: High Mold: Moderate |
Low/medium production of highly complex components |
| Gravity Casting | Medium | Good | Moderate | Product: Moderate Mold: Moderate |
Low/medium production of less complex components |
| Sand Casting | Low | Fair | Moderate | Product: Low Mold: Low |
Low/medium volume production of large, simple components |
| Open Mold Casting | Low | Poor | Short | Product: Low Mold: Low |
Medium to high volume of simple, irregular components or ingots |
| Centrifugal Casting | High but limited to cylindrical shapes | Good | Moderate | Product: Moderate Mold: Moderate |
High-volume production of cylindrical components |
Aluminium Casting Alloys
By carefully combining aluminum with elements such as copper, silicon, magnesium, and zinc, manufacturers can create casting alloys with unique characteristics to meet specific application requirements. On top of varying costs, each alloy offers distinct strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, so making the appropriate choice is crucial for achieving optimal results in the final product.
Image Source: Freepik
Common casting alloys include ADC1, ADC3, ADC10, ADC12, and AC4C. These alloys are classified according to the Aluminium Druckguss system in Europe. “ADC” stands for “Aluminum Die Casting” while “AC” stands for “Aluminum Casting.” The numbers following the ADC/AC designation indicate the specific alloy composition and properties. We will provide a comparison table below and also provide the USA Aluminum Association (AA) designation for your reference.
| Alloy | ADC1 (A413) | ADC3 (A360) | ADC10 (A380) | ADC12 (A383) | AC4C (A356) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum base with 12-13% silicon | Aluminum base with 5-6% silicon | Aluminum base with 9-11% silicon, 3-4% copper, and 0.8-1.2% magnesium. | Aluminum base with 11-13% silicon and 1.2-1.2% magnesium. | Aluminum base with 6-7% silicon |
| Trace Elements | Iron, manganese, copper, magnesium, zinc, and titanium | Iron, copper, magnesium, zinc, and titanium | Iron, manganese, zinc, and titanium | Iron, manganese, copper, zinc, and titanium | Iron, manganese, copper, magnesium, zinc, and titanium |
| Castability | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Machinability | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Corrosion Resistance | Fair | Good | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Hardness | Low | Medium | Medium-High | Medium-High | Medium-High |
| Elongation | Low | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Tensile Strength | Low-Medium | Medium | High | High | High |
| Yield Strength | Low-Medium | Medium | High | High | High |
| Impact Strength | Low | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Typical Casting Process | Die Casting | Die Casting, Gravity Casting | Die Casting, Gravity Casting | Die Casting | Die Casting, Gravity Casting |
The 8 Benefits of Casting with Aluminum
Aluminum casting offers performance and environmental advantages which contribute to its widespread adoption. Its benefits include:
Design Versatility: Aluminum casting enables the creation of custom parts with diverse shapes, sizes, and complexities. From intricate components to large structural elements, each part can be produced with precision and dimensional accuracy, allowing them to maintain optimal performance during assembly, maintenance, and other applications.
Lightweight Results: Aluminum possesses an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, allowing engineers to implement weight reduction without sacrificing mechanical properties.
High Strength and Durability: Aluminum castings exhibit impressive strength and durability, enabling them to withstand demanding conditions over an extended lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that shields it from corrosion. Some aluminum castings are also treated with additional surface finishes or coatings to help them withstand harsh environments and weather conditions with more moisture.
Excellent Appeal: Aluminum castings have a natural luster that offers a sleek, modern appearance, making it ideal for products that require aesthetic appeal.
Rapid Production: Compared to other metals, aluminum alloys can be processed at a faster rate. This translates to shorter lead times and increased efficiency when restocking products to market demands.
Cost-Effectiveness: With fast production minimal finishing requirements, and lower material costs, aluminum casting often provides a high-quality, cost-effective solution that leads to savings, benefiting manufacturers and consumers alike.
Recyclability: Aluminum castings are recyclable so once the discarded products are collected, they can be treated to remove impurities like paint or ink. The extracted aluminum will then re-enter the supply chain to be used for casting or other processes once again. The recycling process consumes significantly less energy than extracting virgin aluminum, making it a sustainable manufacturing method.
The Common Applications of Casting Aluminum
From transportation to home appliances, aluminum casting plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing. Let’s look at some of its common applications which reflect the material’s versatility.
Automotive
Car manufacturers increasingly incorporate aluminum castings into critical components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, suspension parts, brake calipers, and other automotive parts. The lightweight properties of cast aluminum can reduce the overall vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Aluminum's ability to be cast into complex shapes with high precision also enhances vehicle performance and safety.
These requirements are also prevalent in electric vehicles (EVs). By utilizing ADC10 aluminum alloy and gravity casting, Teamsworld has recently created gearbox housings for our client. This component has significantly improved the vehicle’s power-to-weight ratio without compromising structural integrity, allowing us to meet our client’s stringent requirements.
Aerospace
Aluminum casting is critical for modern aircraft, as well as space shuttles and space station structures. Research by the International Journal of Aviation Science and Technology (IJAST) has shown that aluminum alloys usually make up 60-80% of a commercial aircraft’s weight. The aluminum parts are mostly found in the fuselage, wing, and support structures of the airframe. Not only can these aluminum parts reduce weight to increase fuel efficiency and payload capacity, but they also offer the ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh weather conditions for an extended time, boosting the aircraft’s durability.
Kitchenware
Aluminum casting is widely utilized in the culinary industry. With the material’s ability to be molded into various shapes and sizes, manufacturers can create practical kitchen tools that combine functionality and aesthetics, from pots and pans to utensils.
The aluminum cast kitchenware usually has excellent heat conductivity to facilitate even heat distribution and prevent hot spots when cooking. Additionally, aluminum's lightweight nature makes cookware easier to handle, while its durability and corrosion resistance guarantee long-lasting performance.
Lighting
The versatility of aluminum casting enables the creation of various lighting designs, from sleek modern fixtures to traditional chandeliers. Its durability and corrosion resistance also make it ideal for both indoor and outdoor lighting.
Moreover, aluminum has excellent heat dissipation properties that can help to manage the thermal challenges associated with lighting components, such as LED heat sinks. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the lighting fixture.
In collaboration with our client, Teamsworld has created wall luminaires and garden lighting fixtures using die casting techniques and high-performance aluminum alloys. By leveraging advanced equipment, we have achieved various unique, aesthetically appealing surface finishes on these customized fixtures. We also reduced material waste in the process, allowing our client to cut costs through sustainable manufacturing.
Construction
Aluminum castings are increasingly found in the construction industry, especially in structural components and exterior cladding. This is because aluminum alloys provide lightweight properties and great tensile strength that can handle large glass panels and other construction materials. The durability against rust and oxidation also allows it to maintain optimal performance over a long period.
Electronics and Telecommunications
For enclosures and other electronic devices, aluminum protects sensitive internal components from environmental factors while providing structural support and visual aesthetics.
The telecommunications sectors also heavily rely on aluminum castings to ensure the reliable performance of their products, especially for heat sinks, as aluminum can transfer heat away from components to prevent overheating and system failures.
Teamsworld has developed a high-performance heat sink for our client’s critical ICT component. By utilizing a special aluminum alloy with exceptional thermal conductivity (over 150 W/m-K) and leveraging our technology for die-casting, sandblasting, CNC machining, and plating, we managed to improve heat dissipation significantly, saving the hassle of a complete infrastructural redesign.
Medical Components
To be distributed, medical equipment must meet stringent quality and safety standards. Aluminum casting can create complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy, making it essential for manufacturing medical components. Its strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties are also crucial for the safety of patients. With this, aluminum casting can be used to produce prosthetics, surgical trays, equipment housings, etc.
Agriculture
The productivity of agriculture highly depends on the durability and efficiency of machinery. With aluminum castings, agricultural components such as engine housings, gearbox casings, and pump impellers, can benefit greatly from the material’s lightness and strength. What’s more, aluminum’s recyclability can also reduce the carbon footprint of produce, allowing farmers to make an effort toward the industry’s growing emphasis on sustainability.
In the previous year, Teamsworld has assisted a client in enhancing their farm machinery’s engine component. By applying T6 heat treatment to ADC10 aluminum alloy castings, we significantly enhanced the mechanical properties of the parts, including tensile strength, elongation, and hardness. This resulted in improved engine reliability and performance for our client’s equipment.
High-Quality Aluminum Casting Solutions by Teamsworld
Teamsworld is a leading provider of exceptional aluminum castings, boasting over 20 years of industry expertise. We’ve delivered over 2 million components to clients worldwide, including the US, Germany, and Asia, with a proven track record of timely deliveries and prime products that exceed expectations, earning us ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949 certifications that underscore our commitment to quality and efficiency.
On top of that, we also focus on sustainable practices as a B-Corp-certified manufacturer. We leverage a cloud-based project management platform to streamline processes and reduce our carbon footprint throughout the entire production.
Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facility houses 20 sets of advanced die casting machines from renowned brands such as TOSHIBA, UBE, TOYO, and Italpresse. This robust equipment, combined with our skilled workforce, enables us to produce a vast range of aluminum castings with unmatched precision and efficiency.
From design conceptualization to finished product, Teamsworld offers a comprehensive range of services including prototyping, die casting, machining, finishing, and assembly. Our experts will work closely with you to develop tailored aluminum casting solutions that meet your specific requirements. Contact Teamsworld today for a free consultation and bring your product vision to life!