Comprehensive Guide to Automotive Die Casting: Materials, Applications, and Market Trends
Automotive die casting is a high-precision manufacturing process widely used to produce complex metal components for vehicles. By injecting molten metals such as aluminum, magnesium, or zinc alloys into reusable steel molds under high pressure, manufacturers can create lightweight yet durable parts with excellent dimensional accuracy.
As global demand for fuel efficiency and electric vehicles grows, die casting has become essential in reducing vehicle weight while maintaining structural strength. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global automotive parts die casting market is projected to grow from $48.99 billion in 2025 to $66.14 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.19%. This growth is driven by the rising adoption of lightweight materials, sustainability initiatives, and the increasing penetration of electric vehicles.
Beyond performance, automotive die casting also contributes to sustainability goals through high material utilization rates (often above 90%) and reduced machining waste. This combination of efficiency, strength, and eco-friendliness makes die casting a cornerstone of modern automotive manufacturing.
In this guide, we will explore the key advantages of automotive die casting, the metals commonly used, its applications in critical vehicle systems, and how quality control ensures long-term reliability.
Key Advantages of Automotive Die Casting for Manufacturers
Automotive die casting offers numerous benefits that make it a preferred manufacturing process for vehicle components. From efficiency to precision, the process addresses the automotive industry's high standards for quality, performance, and sustainability.
1. Short Production Cycle
Die casting is renowned for its rapid production cycle, thanks to fast mold filling and quick solidification of metals. This efficiency reduces lead times and allows manufacturers to produce more parts in less time, lowering costs. For example, aluminum engine blocks can be die-cast in under 10 minutes per piece, significantly faster than traditional sand casting methods.
2. High Part Strength
Die-cast parts demonstrate exceptional mechanical strength, enhancing durability and reliability. This is critical for high-stress automotive components, such as chassis structures, suspension brackets, and high-strength alloy wheels that must withstand rigorous driving conditions. Automotive OEMs increasingly use die-cast aluminum and magnesium alloys for weight-sensitive yet load-bearing parts.
3. Capability to Manufacture Precision Parts
Precision is vital in automotive manufacturing. Die casting allows for tight tolerances and intricate designs, ensuring that each component meets exact specifications. This precision is especially important for engine components, transmission housings, and brake calipers, where even minor deviations can affect vehicle performance.
4. High Material Utilization Rate
One of die casting’s major advantages is its high material utilization rate, often exceeding 90%, meaning minimal waste during production. Compared with machining from solid blocks, die casting significantly reduces scrap, lowering material costs and supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
5. Freedom of Shape Design
Die casting enables the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible with other processes. Designers can innovate without compromising functionality or aesthetics—examples include intricately shaped dashboards, housings for electronic modules, and lightweight structural brackets.
6. High Production Efficiency
By combining fast cycles, precision, and material efficiency, die casting achieves high production efficiency. Mass-produced components maintain consistent quality, and even small cost savings per part can translate into substantial reductions across large production volumes, making it ideal for OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
In summary, automotive die casting is indispensable for manufacturers seeking fast, precise, strong, and environmentally responsible production. Its ability to deliver high-quality parts at scale aligns perfectly with the automotive industry’s demand for performance, efficiency, and innovation.
Common Metals for Automotive Die Casting
In automotive die casting, choosing the right metal is crucial for balancing weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and cost. The most common metals include aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys, each with distinct advantages for specific automotive applications.
| Metal | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal conductivity | Engine blocks, transmission housings, EV battery enclosures, structural components | Reduces vehicle weight, improves fuel efficiency, supports EV adoption |
| Magnesium | Extremely light, strong, good vibration damping | Steering wheels, seat frames, electronic housings | Ideal for weight-sensitive parts, reduces overall vehicle mass |
| Zinc | High strength, ductility, excellent surface finish | Door handles, locks, interior trim, small brackets | Enables intricate shapes, cost-effective, corrosion-resistant |
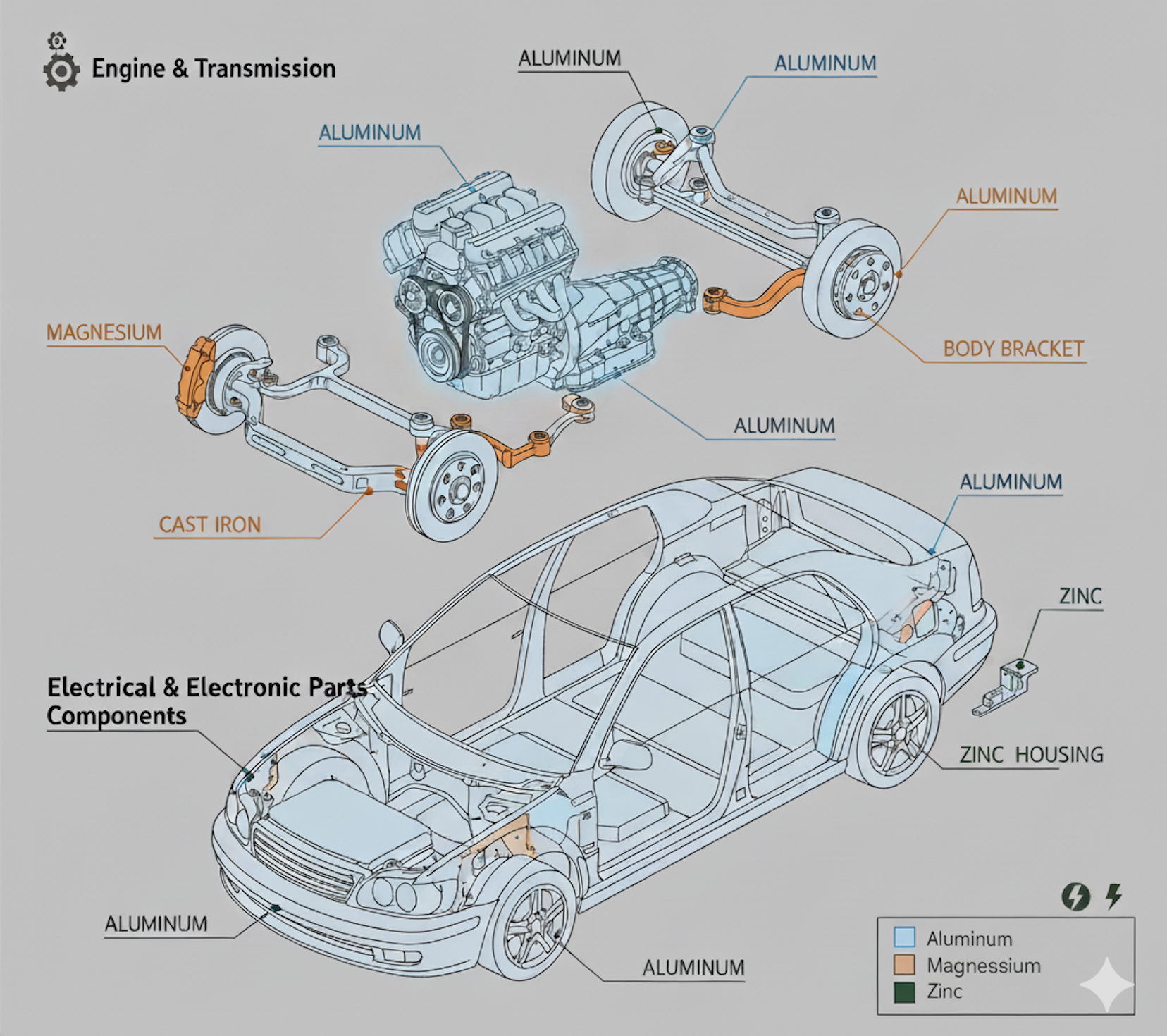
Applications of Automotive Die Casting
Die casting is widely applied across numerous vehicle systems, from structural components to electronic modules. Its precision and efficiency make it essential for both conventional vehicles and electric vehicles (EVs). Key Applications Include:
1. Engine & Transmission Components
Automotive die casting is widely used in engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission housings due to its high precision, excellent thermal conductivity, and structural strength. Aluminum die casting enables lightweight automotive parts, reducing overall vehicle weight while maintaining durability and performance.
2. Suspension & Brake Systems
Suspension brackets and brake calipers require durable, load-bearing components. Die-cast magnesium and aluminum alloys provide lightweight strength, enhancing vehicle handling, braking efficiency, and overall safety.
3. Body & Chassis Parts
Door frames, body brackets, and structural reinforcements are commonly produced using die casting. The process allows for complex shapes, tight tolerances, and consistent quality, improving assembly efficiency and reducing manufacturing costs.
4. Electrical & Electronic Components
Modern vehicles, especially electric vehicles (EVs), rely on die casting for battery housings, sensor brackets, and electronic module enclosures. Die-cast components ensure precision, thermal management, and lightweight design, supporting the growing demand for high-performance automotive electronics.
Automotive Die Casting Application - ALUMINUM, MAGNESIUM, AND ZINC USAGE
Quality Control of Automotive Die Casting
Ensuring consistent quality in automotive die casting is essential, as die-cast components must withstand mechanical stress, high temperatures, and vibration throughout the vehicle lifecycle. Implementing rigorous quality control measures guarantees high-strength, reliable automotive parts that meet industry standards.
1. Dimensional Inspection
Precision is critical in automotive die casting. Using laser scanning and coordinate measuring machines (CMM), manufacturers verify that each part meets tight tolerances (often ±0.1 mm), ensuring proper fit and optimal performance in assemblies.
2. Material Testing
Alloy properties are tested through hardness, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance evaluations. These tests confirm that aluminum, magnesium, and zinc die-cast components meet the mechanical and durability requirements of modern vehicles.
3. Process Monitoring
Automated sensors continuously monitor mold temperature, injection pressure, and cooling rates during die casting. This proactive process control minimizes defects such as porosity, warping, and dimensional inconsistencies, enhancing overall production quality.
4. Standards & Certification
Adherence to IATF 16949, ISO 9001, and ISO 14001 ensures that all die-cast components comply with global automotive quality standards. Certifications provide confidence across the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to finished precision components.
Trends in Automotive Die Casting
Automotive die casting has become a cornerstone in modern vehicle manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, strength, and design flexibility. As the automotive industry evolves, die casting continues to play a pivotal role in meeting the demands for lightweight, durable, and efficient components.
Market Growth and Demand
The global automotive metal die casting market was valued at approximately USD 53 billion in 2025 and is projected to exceed USD 109.23 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5%. This growth is driven by several factors:
Shift Towards Lightweight Materials: The automotive industry is increasingly adopting lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs): The growing popularity of EVs necessitates the use of lightweight and durable components to improve performance and battery efficiency.
Advancements in Die Casting Technology: Innovations in die casting processes, such as Gigacasting, have led to improved precision and the ability to produce complex geometries, expanding the scope of applications.
Technological Advancements
Recent technological advancements have further solidified die casting's role in automotive manufacturing:
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC): HPDC allows for the rapid production of high-strength components with excellent surface finishes, making it ideal for structural parts.
Cold Chamber Die Casting: This method is particularly suited for metals with high melting points, such as aluminum and magnesium, enabling the production of lightweight and heat-resistant components.
3D Printing Integration: The integration of 3D printing with die casting is facilitating the creation of complex molds and cores, reducing lead times and costs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a key consideration in modern manufacturing. Die casting contributes to environmental goals through:
High Material Utilization Rates: Die casting processes often achieve material utilization rates exceeding 90%, minimizing waste.
Energy Efficiency: Advancements in die casting technology have led to more energy-efficient processes, reducing the overall carbon footprint.
Recyclability: The metals used in die casting, such as aluminum and magnesium, are highly recyclable, supporting circular economy initiatives.
In conclusion, automotive die casting remains a vital technology in the automotive industry, offering solutions that align with the demands for quality, efficiency, and sustainability. Its ability to produce high-strength, lightweight, and complex components positions it as a key enabler in the future of automotive manufacturing.
For businesses looking to streamline their automotive supply chain and source high-quality die-cast components, Teamsworld offers a robust platform connecting manufacturers across Asia with global automotive brands. From precision aluminum engine blocks to lightweight EV components, our experts provide tailored solutions to meet your production and quality requirements.