Aluminum vs Magnesium: The Future of Lightweight Automotive Die Casting
The future of automotive engineering is being forged in a crucible of innovation, where the demand for lighter, more efficient vehicles has never been more urgent. This pivotal shift, driven by strict environmental regulations and the explosive growth of electric vehicles (EVs), has made lightweighting a competitive imperative. The solution is found in advanced automotive die casting techniques. This comprehensive guide dives into the core of this transformation, examining how aluminum and magnesium are reshaping vehicle design. We will compare their unique properties and explore their critical role in creating the next generation of sustainable, high-performance vehicles.
Why Lightweight Materials Matter in Automotive Design
The impact of vehicle weight on energy efficiency cannot be overstated, particularly in electric vehicle applications where every gram counts toward maximizing battery range. The US Department of Energy's research on lightweight materials for cars and trucks confirms that using lightweight materials in electric vehicles can offset the weight of power systems such as batteries and electric motors, improving efficiency and increasing all-electric range. Reducing vehicle weight by 10% can improve fuel economy by approximately 6-8% in conventional vehicles and extend EV range by similar margins. This direct correlation between weight reduction and energy efficiency makes lightweight materials a critical component in achieving regulatory compliance and market competitiveness.
Global regulations continue to drive the lightweight agenda, with increasingly stringent Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States, European Union emissions regulations, and similar mandates worldwide. These regulatory frameworks create a compelling business case for adopting advanced lightweight materials, as non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties and market access restrictions.
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Tier 1 suppliers are responding to these pressures by fundamentally reimagining their material selection strategies. Traditional steel-dominant architectures are giving way to multi-material approaches that strategically deploy aluminum, magnesium, and advanced composites where they provide maximum benefit. This shift represents not merely a material substitution but a complete rethinking of vehicle architecture and manufacturing processes.
Aluminum Die Casting in the Automotive Industry
Aluminum is the leading lightweight metal for automotive applications, valued for its exceptional properties that make it perfect for structural components.
Core Strengths
With a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³, aluminum offers significant weight savings over steel while maintaining an excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Its natural corrosion resistance is a major advantage, eliminating the need for extensive protective coatings and simplifying the manufacturing process.
Economics & Sustainability
The sustainability credentials of aluminum are particularly compelling, with recycling rates exceeding 90% in automotive applications. Notably,around 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use today, according to The Aluminum Association. Recycled aluminum requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce primary aluminum, creating closed-loop manufacturing systems that align with the principles of a circular economy. This recyclability, combined with aluminum's durability and corrosion resistance, establishes it as a cornerstone material for sustainable automotive manufacturing. Thealuminum industry's recycling efforts in the U.S. save more than 90 million barrels of oil equivalent each year, demonstrating the significant environmental impact of choosing recyclable materials.
Pioneering Technology
Aluminum's potential is best showcased by revolutionary technologies like Tesla’s Gigacasting, which uses high-pressure die casting to create large, single-piece structural components. This not only reduces part count but also eliminates welding operations and improves structural integrity. Beyond gigacasting, aluminum is widely used for powertrain housings in electric motors, battery cooling systems, and safety-critical chassis components.
Magnesium Die Casting in the Automotive Industry
Magnesium is the lightest structural metal, roughly 30% lighter than aluminum. This makes it ideal for applications where every gram of weight reduction is critical, such as in steering components and transmission housings. However, magnesium is more expensive and has lower corrosion resistance, limiting its use to high-value parts where its weight advantage justifies the cost. Its recycling infrastructure is less mature than aluminum's, but ongoing research is improving its sustainability profile.
Key Properties & Advantages
Magnesium's exceptional weight advantage makes it particularly attractive for applications where weight reduction directly impacts vehicle dynamics. Its high specific stiffness and excellent damping properties also make it ideal for parts that require vibration absorption.
Cost & Challenges
The cost equation for magnesium is more challenging than aluminum due to raw material prices typically being 2-3 times higher. Additionally, its susceptibility to corrosion requires specialized surface treatments, adding complexity and cost to manufacturing processes.
Applications
Current automotive applications for magnesium focus on areas where weight reduction provides maximum benefit: steering wheel armatures, transmission housings, and seat structures. These targeted uses demonstrate magnesium's potential while acknowledging its current limitations.
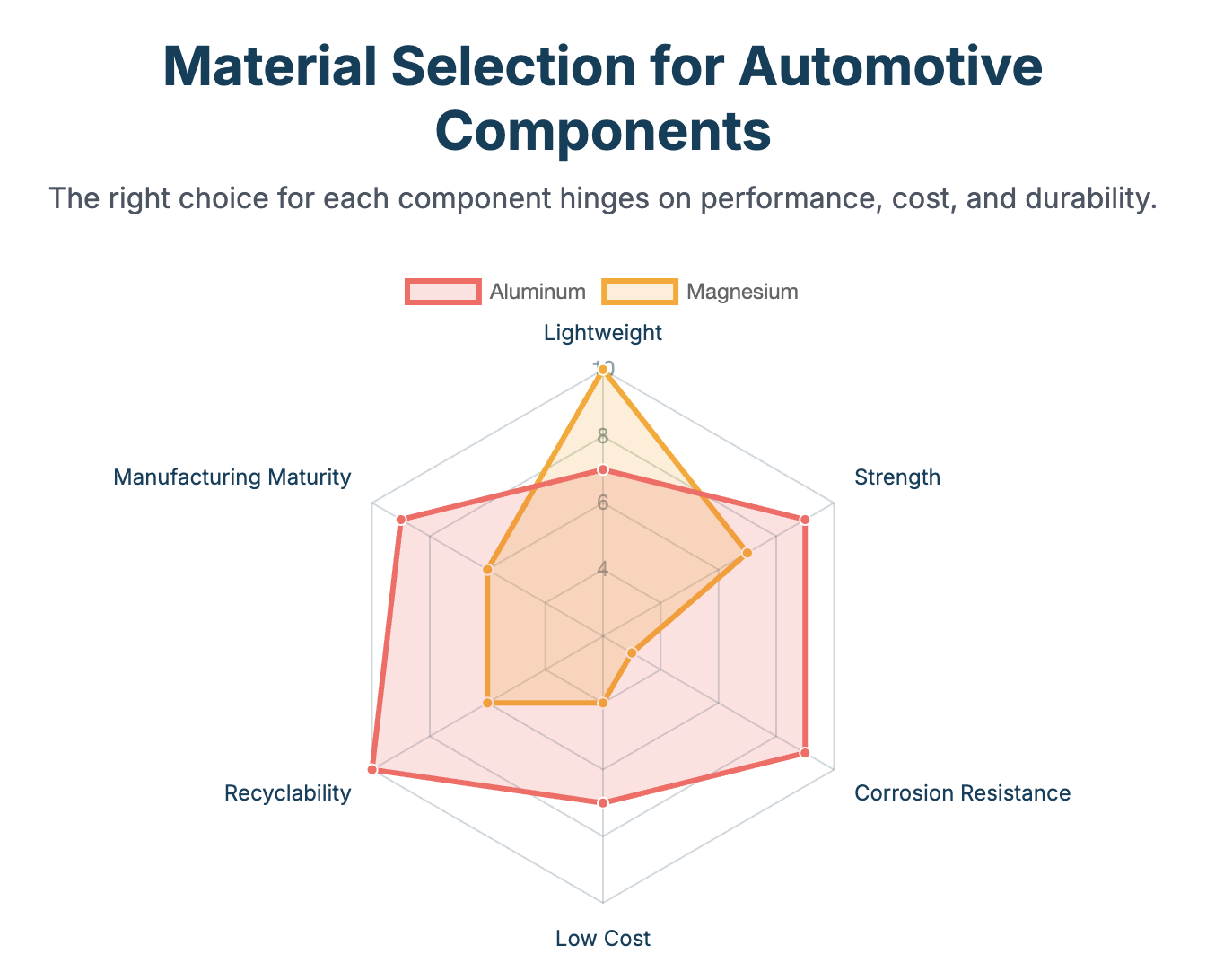
Aluminum vs Magnesium – A Direct Comparison
| Property | Aluminum | Magnesium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ~2.7 g/cm³ | ~1.8 g/cm³ |
| Strength | High | Medium-High (requires alloying) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low (requires surface treatment) |
| Cost | Medium | High |
| Recyclability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Manufacturing Maturity | High | Medium |
The strategic selection between aluminum and magnesium requires careful consideration of application-specific requirements, performance criteria, and cost constraints. Rather than viewing these materials as competitors, successful automotive manufacturers adopt complementary approaches that leverage each material's strengths while mitigating their weaknesses.
OEMs increasingly implement hybrid material strategies that utilize aluminum for primary structural applications where strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness are paramount, while deploying magnesium in targeted applications where maximum weight reduction justifies premium costs. This nuanced approach optimizes overall vehicle performance while managing development and manufacturing risks.
Sustainability and Recycling Considerations
Aluminum's Circular Economy
The sustainability of lightweight materials encompasses their entire lifecycle. Aluminum’s high value and infinite recyclability make it ideal for a circular economy. Its global recycling systems are well-established, with over 75% of all aluminum ever produced still in use today. This mature infrastructure ensures high recycling rates and supports closed-loop manufacturing.
The Challenge of Magnesium
Magnesium recycling presents greater challenges and its recycling rates currently lag behind aluminum. However, ongoing research into improved recycling techniques promises to enhance its sustainability profile. Developing a robust recycling network for magnesium is a key industry focus, which would unlock more applications for this ultra-lightweight metal.
Material selection decisions made today will determine sustainability performance for decades to come. Companies that invest in recyclable material systems and closed-loop manufacturing will gain a competitive advantage as sustainability regulations and consumer preferences evolve.
Applications in EVs and Sustainable Mobility
Aluminum Applications in EVs
Aluminum’s excellent electrical conductivity and thermal management properties make it ideal for EV battery housings and motor casings. Its use not only reduces weight but also effectively dissipates heat, which is crucial for prolonging battery life. Large-scale aluminum die casting (like Tesla's Gigacasting) consolidates multiple structural components into a single part, which simplifies assembly and improves rigidity.
Magnesium Applications in EVs
Magnesium finds targeted applications where maximum weight reduction provides the greatest benefit. It is used in interior structural components like dashboard frames and seat frames, as well as auxiliary systems housings. In these non-safety-critical areas, magnesium's lightweight properties contribute directly to overall vehicle efficiency without compromising core integrity.
Material Innovation as a Competitive Advantage
The future of automotive lightweighting is not about choosing between aluminum and magnesium, but about strategically deploying both. A multi-material design approach leverages each material’s strengths, addressing specific performance and cost requirements simultaneously. OEMs that master this will gain a significant competitive advantage through improved vehicle performance and enhanced sustainability.
The next 5-10 years will bring significant innovations in lightweight materials, including hybrid casting processes and advanced recycling systems. Companies that invest in these emerging technologies will be best positioned to lead the sustainable mobility revolution. The automotive solution on lightweighting journey embodies a fundamental shift toward sustainable manufacturing and innovative design thinking.
Partner with Teamsworld for Your Lightweight Die Casting Solutions
As the automotive industry accelerates toward sustainable mobility, choosing the right manufacturing partner is critical. Teamsworld combines decades of expertise in both aluminum and magnesium die casting with cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices. Our comprehensive capabilities, from prototype to high-volume production, ensure your lightweight components meet the most demanding performance and quality standards. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you reduce vehicle weight, improve performance, and accelerate your sustainability goals.